Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by increased blood sugar.
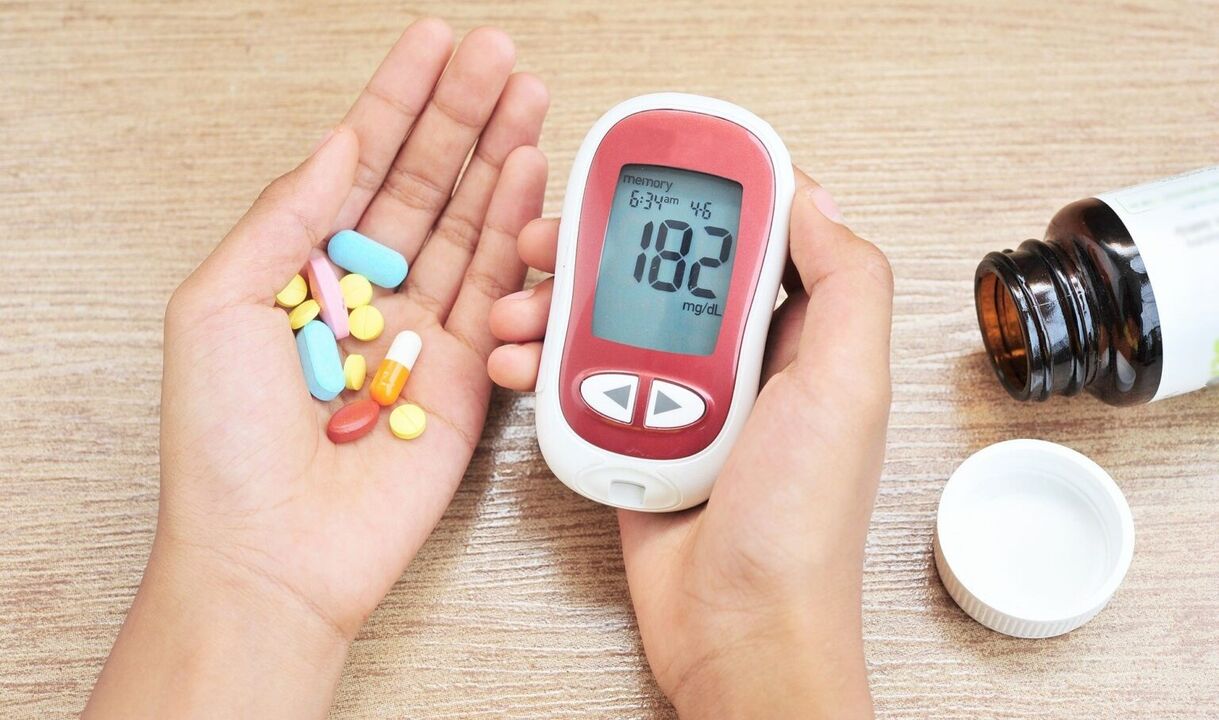
The disease occurs due to a defect in insulin production, which is a defect in the action of insulin or both factors. In addition to elevated blood sugar levels, the disease also develops through the release of sugar in the urine, large amounts of urination, increased thirst, diseases of fat, protein and mineral metabolism, and the development of complications.
type
- Type 1 diabetes (autoimmune, idiopathic): The beta cells of the pancreas are destroyed and insulin is produced.
- Type 2 diabetes - a major deficit in insulin production that is accompanied by tissue insensitivity to or insensitivity to insulin.
- Diabetes develops gestational sugar during pregnancy.
- Other types:
- Genetic defects;
- Diabetes caused by drugs and other chemicals;
- Diabetes caused by infection;
- Pancreatitis, trauma, pancreatic removal, acromegaly, Izenko-Kushinka, thyroid toxicity, etc.
Severity
- Simple current: no complications.
- Average severity: Eyes, kidneys, and nerves are damaged.
- Severe current: complications of diabetes.
Symptoms of diabetes
The main symptoms of the disease include:
- Urinate heavily and thirst;
- Increased appetite;
- universal weakness;
- Due to the emergence of immunodeficiency, skin lesions (such as vitiligo), vagina and urinary tract are particularly observed in non-contaminated patients.
- Blurred vision is caused by changes in the mediator of the eye.
Type 1 diabetes usually starts from an early age.
Type 2 diabetes is usually diagnosed in people over 35-40 years old.
Diagnosis of diabetes
The diagnosis of the disease is based on blood and urine tests.
For diagnosis, determine the concentration of glucose in the blood (the important case is to repeatedly determine the elevated sugar content and other days).
The results of the analysis are normal (without diabetes)
Fasting or 2 hours after the test:
- Venous blood-3. 3–5. 5 mmol/l;
- Capillary blood-3. 3–5. 5 mmol/l;
- Blood plasma - 4–6. 1 mmol/l.
Analysis of the presence of diabetes
Empty :
- Venous blood exceeds 6. 1 mmol/l;
- Capillary blood exceeds 6. 1 mmol/l;
- Venous plasma exceeds 7. 0 mmol/L.
At any time of day, no matter what time you eat:
- Venous blood exceeds 10 mmol/L;
- Capillary blood exceeds 11. 1 mmol/l;
- Venous plasma exceeds 11. 1 mmol/L.
The levels of glycated hemoglobin in diabetes exceed 6. 7-7. 5%.
The content of C peptide allows you to evaluate the functional status of beta cells. In patients with type 1 diabetes, insulinoma patients usually have a decrease in type 2 diabetes, and insulinoma patients have a sharp increase.
By type 1 or type 2, the concentration of immunoreactive insulin is reduced or increased.
In the context of acute disease, injury, or surgical intervention, determining the concentration of glucose in the blood is not performed in the context of short-term administration, which increases the concentration of glucose in the blood (adrenal hormone, thyroid hormone, thyroid hormone, β reagent, β reagent, β reagent, etc. ). liver.
Glucose in urine occurs only after exceeding the "renal threshold" (approximately 180 mg% 9. 9 mmol/L). Significant fluctuations in thresholds and trends with age are characteristic. Therefore, the definition of glucose in urine is considered an insensitive and unreliable test. This test is the total reference point for a significant increase in sugar (glucose) in the blood, and in some cases, is used to observe the kinetics of the disease every day.
Treatment of diabetes
Proper nutrition in physical exercise and treatment
In a large proportion of diabetics, dietary recommendations were observed and significantly reduced 5-10% of the initial weight of weight, and the glycemic index improved the standard. One of the main conditions is the regularity of physical fatigue (for example, walking for 30 minutes a day and swimming for 1 hour 3 times a week). With the concentration of glucose in the blood >13–15 mmol/L, sports activities are not recommended.
For a duration of not more than 1 hour, mild and moderate physical fatigue requires additional carbohydrate use (15 g of easy-to-digest carbohydrate every 40 minutes). With moderate physical fatigue continuing for more than 1 hour of exercise and strengthening exercise, it is necessary to reduce the insulin dose by 20-50% for the next 6-12 hours after physical exercise and for the next 6-12 hours.
The diet for diabetes treatment (Table 9) is designed to enable carbohydrate metabolism and prevent fat metabolism.
Treatment with insulin preparations
Insulin treatment of diabetes is divided into 4 categories according to the time of action:
- Ultra - Koro action (start of action - after 15 minutes, the duration of the action is 3-4 hours).
- Move quickly (start of the action - after 30 minutes - 1 hour; duration of the action 6-8 hours).
- The average duration of the action (the beginning of the action is 1-2. 5 hours, and the duration of the action is 14-20 hours).
- Long-term action (the beginning of the action is 4 hours later; the action lasts up to 28 hours).
The appointment mode for insulin is strict and is selected for each patient of a dialer or endocrinologist.
Methods for introducing insulin
When insulin is introduced at the injection site, it is necessary to form skin folds so that the needle can enter the skin, not into the muscle tissue. The skin folds should be wide, and if the thickness of the skin fold is less than the length of the needle, the needle should enter the skin at an angle of 45°.
When choosing a place to inject, compacted skin areas should be avoided. The injection site cannot be changed non-systemic. Do not inject under the skin of your shoulders.
- Short-acting insulin preparations should be used for subcutaneous fatty fibers in the anterior wall of the abdomen 20-30 minutes before feeding.
- Introduce long-acting insulin preparations into the subcutaneous fatty fibers of the thigh or buttocks.
- Prior to eating, if necessary, during or immediately before eating, super insulin injections.
Calories and physical activity increase insulin absorption, while colds decrease.